Fintech
Stripe guide
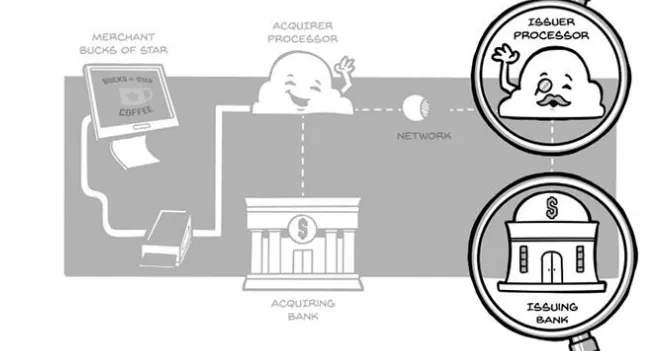
4 players involved in online trans
- Cardholder: person who pays
- Merchant: business owner(client of Solidgate)
- Acquirer: bank who processes payment(Visa, MasterCard)
- Issuing bank: bank of cardholder
Payment Methods
- Credit Cards
- Digital wallets(Apple/Google Pay)
- Bank debits
- Buy now pay later services
- Cash via ATM
Taxes
- Indirect(customer pays)
- US - sales tax
- EU - value-added tax(VAT)
- Canada - goods and services(GST)
- Japan - consumption tax(JCT)
- Physical goods - depends on shop-from. ship-to, product category
- Online - based on local laws
Offline sales - 90% of all sales
- users should have same experience for on(off)line
- payments methods and benefits must be the same
- it its good practice to support magnetic stipe, but it less safe
SaaS
- flexible subsc logic(different types of payment: per month, per order)
- invoice problem: it is must have for big purchases, but must be country based
- minimize failed payment attempt
- send failed payment emails
- send schedule emails
- add backup payment methods
Marketplace
- main problem: you becoming bank-like struct that moves money from buyers to sellers
- problems
- you need to know many info about customers(not to get penalty), but also it makes onboard process more complicated
- moving money
- one-to-one: one customer - one seller
- one-to-many: one big pay - several sellers
- holding: customers pays - seller receives with delay
- account debits: platform takes fees
- subscriptions
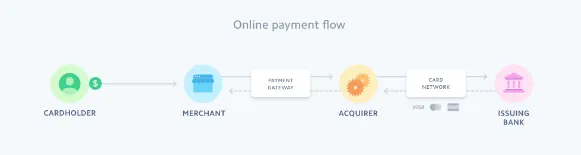
Transaction flow:
- checkout completion -> fraud protection -> network acceptance Checkout Form
- collects minimal data to make operation
- fast loads, minimal fields, autofill support, UI/UX
- Apple/Google Pay support
- support of local currencies and methods + adapt to local standarts Fraud
- chargback is bad for marchant, cause it must pay chargback fees as well as moneyback
- WAYS TO DETECT
- rule-based
- block transactions from IP, Country, by Amount
- AI
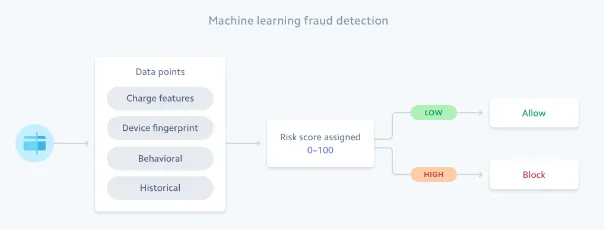 Net acceptance
Net acceptance
- rule-based
- bank will check info and decide to accept/denay
- this decision is made by amount of info and amount of prev operations
PCI standards - security guidelines
-
tokenization
-
3D Secure
-
Anatomy of Swipe
Marqeta - company to create cards and payment рахунки Stripe - money gateway
Visa/MasterCard - Payment Networks of banking system
Money Route(mostly happens by Dual-Messaging)
- Authorization(ISO 8583)(~3 seconds time delay)(holds money)
- message goes from terminal to Acquire Processor with data like(amount, location, card number, Merchant type)
- network provider detected and rerouted
- first six digets are detected(bin - Bank Identification Number)
- bank checks data and decides to approve/not
- is it proper bank
- is card active
- is enough money
- is card can be used
- is it legit activity
- Clearing/Capturing(moves money)(manual/auto)
- Settlement - post moving process when all money moved
- During settlement Payment Network will take fees and send bills
- Merch Acquirer takes it fees monthly
- when settled operation will be changed from pending to completed A number of parties are involved in money transaction:
- card networks - visa, MC
- merchant acquirer - company that give interface to make payments for merchants
- issuers - banks
chargeback(should be bellow 1%)
- zero liability police insures that customer can mark transaction as fraudulent for free and have moneyback(but card change may/must be needed)
- 30% of reports - stolen cards
- flow
- report -> card freeze -> bank calls for chargeback via Card Net -> transaction goes back to customer -> Merchant is requested to explain and send chargeback with-in 45 days
- merchant reaction
- do nothing and pay
- dispute(impossible if transaction done by magnetic stripe || not likely if CVV won’t present)
- pay fees to dispute
- show proves
- bank covers cost
3D Secure - 2fa like method to make transaction more secure(EU more | US less) EMV - safety standarst(manged by EMV co.)
- 1.0 - done by pin code
- 2.0 - done buy “Yes” button inside mobile app
know your customer
- get some info from your client so you can verify and identify him
interaction types
- swiping - magnetic stipe
- dipping - chip
- tapping - phone transaction
- entering - pc transaction
card network(card scheme)
- main job to pass info from one side to other
- sets rules for sides + format of communication(ISO8583) + format of dealing with problems
- provide a license to use
- TWO TIPES
- Open(Visa and MC)
- don’t do more than just transfer and marketplace function + don’t have favorites
- Closed(American Express)
- may have own cards and banks
- Open(Visa and MC)
- make money buy taking fees per transaction OR with own brand cards
transaction types
- debit | PIN Debit Purchase
- lower fees + pin verification
- Single Message
- credit | Signature Purchase
- higher fees + additional verification
- Dual Message
- auth
- clearing
- if there was fees they will be processed on this stage
- atm
- charges fees from client
- Single Message
neo-bank OR challenger banks - online only banks(mobile-first)
- offers lower fees
- often this is not banks but tech programs that operates under some banks(unregulated often)
banks - only them can move money
- functions
- issue cards to people
- serve as banks to merchants
- facilitate movement of real money
- TYPES(one bank can be both)
- issuing banks
- give cards to people
- know your customer(KYO)
- acquiring banks
- serve as bank to merchants
- legitimate merchants
- issuing banks
- TYPES by interchange
- regulated - big banks(restrictions by law)
- unregulated
each card has BIN(6 digits to identify bank)
taking payments
- work with bank directly
- harder but can give more benefits(lover fees, more customizability, less limitations, use other products to manage payments and hardware, percentage based fees, fast money settlement)
- MINUSES
- paper work
- manage frauds
- work with bank through ISO(independent sales org) - have license to sell banks services
- work with payment facilitator(PF, PayFac) - very quick and gives starter pack(like devices)
- often have fixed pricing
- give tools to deal with chargebacks
- MINUSES
- fixed pricings can be high
- sometimes low variety of options
- all money movement can take days
- flat fees
- (PSP) payment service provider(Stripe) - aggregator for online payments
- Buy Now Pay Later(BNPL) - buyer pays tp some 3d party company for some period, while seller get his money right away(high fees)
best practice - have a merchant experience team to help your merchants and etc flat fees - some amount of money not a percentage
BUSINES CAN CREATE THEIR OWN BRANDED CARDS co-brand partner - brand which is marketing card(Delta airlines who uses American Express card)
program manager - party that controls operations and operations
- frauds, settlements etc
issuer processors - licensed party that holds MIPs of VIPs(hardware from MC or Visa to communicate with them)
- approving/declining + integration and management with merchant + reporting to merchant and bank
JIT Funding(just in time funding) - possibility to smbd to control over some operation in real time(глово може управляти транзакціями кур’єрів наприклад)
KYC(know your customer) - practice to attach identity to user
- usually collect bare minimum to further chek public info about customer
- for gift cards there is procedure that spending is not require KYC, but loading money do
- its important to add another verification method for people that don’t have public info AS WELL AS it’s a good practice to use multiple KYC providers
- for small business there is a practice to check an owner
Credit VS Debit Cards
- Both
- sexteen-digit card number
- expiration date
- cvv
- name?
- Credit
- 30days loan with charge at the end of period
- usually user pays monthly fees
- can be harder to get
- Debit
- lower payment rates for Merchants
- less preferred because of risks that user won’t have money to pay for hotel of smth else
- becoming more popular
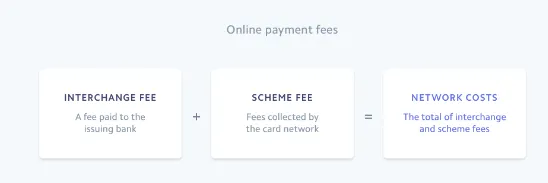
Interchange - fee that Merchant pays to Bank of the card owner that payed
- different for each bank and network but main differents are:
- type of business
- each merchant is classified with MCC(merchant category code) - depends on industry
- some categories may be more fraudulent and riskier + different categories have different money amount flow
- each merchant is classified with MCC(merchant category code) - depends on industry
- type of card
- debit and prepaid - “good funds model”(works with real money)
- different because of Network fees(because of Dual and Single Messaging)
- INDUSTRY PRACTISE
- make all debit purchases be in credit mode(some cards can be both debit and credit) as well as turn off pin verif(PIN-less Debit)
- also high fee can be because of Company card vs consumer
- credit fees are caused by people spend more + bank lowers chargeback
- ”regulated” banks have less fees because of law restrictions
- fast banks can have larger fees
- if merchant provide Track 3 data(show all bought products) it can have less fees
- some approach is to create bank+merchant card with super small or no fees(privat label cards)
- type of business
Moving money without network
- ACH(automated clearing house) - bank-to-bank via non-profit org “Clearing House”
- batch based
- used for online payments
- slower
- not all banks are supporting
- Direct Deposit
- often ACH transfer that can be electronic checks analog
- used to pay check for employees
- Peer-to-Peer
- usually based on ACH
- can be virtually immediate but on practice p2p app may move money couple of days
- Zelle
- if users from the same bank send each other money it happens instantly without settlement
- Zelle makes such behavior similar for payments between banks OTHERWISE such transactions are treated as full money moving process
- bank must be connected to Zelle network
- user may need to login and use ids like phone number
- Wire Transfer - way to move money(large amounts) securely between banks
- faster then ACH
- need confirmation and more expensive fees
- need human operator to confirm transaction
- RTP(rela-time payments) - smth like wire transfer but without confirmation and for smaller amount
- near instant
- low fees
- works on push technology
Push-to-card OR OCT(original credit transaction), because no purchase goes along
- fast(instant) because money available to spend instantly(and all moving process is done in background)
- debit based
Virtual Cards
- quick creation process
- online payments of Apple/Google Pay
Expense Reports Alternatives
- OLD WAY
- person purchase from personal card that connected to system
- each purchase is tracked and at the end of the month revisions, corrections and payoffs are made
- PROBLEMS
- can’t limit spends in real time
- EARNINGS // SaaS
- NEW WAY
- person gets virtual card with already set budget + card have one time spend limit
- alternatively person can pay with personal card and then have compensation with in app request
- EARNINGS // Interchange fees